Get Appointment
- contact@wellinor.com
- +(123)-456-7890
Blog & Insights
- Home
- Blog & Insights
By: Saikrishna Madupu – Sr Devops Engineer
Ansible by Red Hat is the de-facto tool used by organizations for automated configuration management. It is commonly used for use cases around infrastructure deployment and post deployment actions, application deployments, and for infrastructure operations and lifecycle tasks.
In the following blog, we will cover some examples ansible callback plugins, which help us track events around playbook executions. You can use these plugins for notification of task failures, job statuses, etc.
Features:
- Stdout plugins
- Other Plugins (also includes notification plugins & aggregate plugins in general)
A complete list of available plugins can be viewed from terminal:
ansible-doc -t callback -l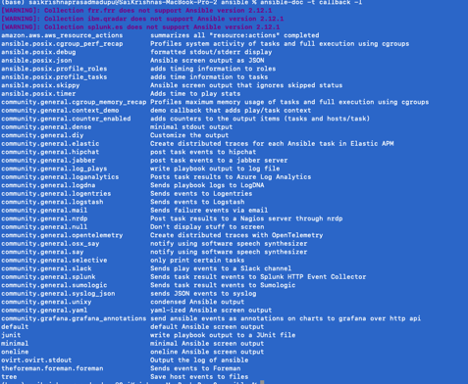
Stdout_plugins:
- This can be configured by adding stdout_callback plugin as a parameter in your ansible.cfg under defaults section. These plugins are limited to use one at a time.
- Syntax:
[defaults]
stdout_callback = actionable- Some stdout_plugins are listed below:
| Name | Description |
| Actionable | Changed/failed status |
| Default | Default o/p |
| debug | Readable stderr & stdout |
| Dense | Overwrite o/p rather than scrolling |
| Json | Json o/p |
| Minimal | Task details with proper format |
| Selective | o/p for tagged task |
| Skippy | Doesn’t show o/p for skipped hosts |
| Oneline | Similar to Minimal but in one line |
Examples of usage:
Actionable:
This plugin is deprecated.
Op:
- community.general.actionable has been removed. Use the 'default' callback plugin with 'display_skipped_hosts = no' and 'display_ok_hosts = no' options. This feature was removed from community.general in version 2.0.0. Please update your playbooks.
Debug:
By enabling debug plugin we don’t need to register output and use again debug module in our playbooks.
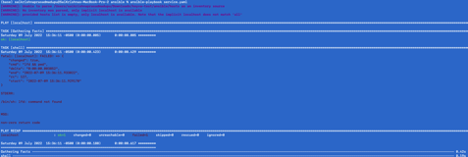
Default:
Displays standard error in human readable format

Dense:
It overwrites o/p and only shows two lines as shown below.

JSON:
Prints o/p in json format and we see the entire o/p.
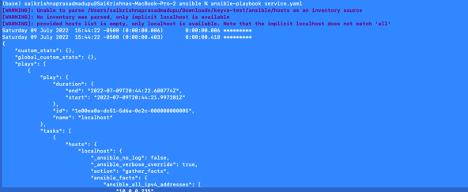
Minimal:
It is quite similar to default,

Selective:
Selective plugin shows o/p for tasks that got executed successfully that are tagged with print_action

Skippy:
It doesn’t show o/p for the tasks that got skipped, when a task is not executed for any sort of host it will not be displayed as skipped likewise default do in cases.

Oneline:
It shows o/p of command in one format as shown below.

Other plugins:
- There are several other plugins which can send alerts in case of job failures to slack channels, records job execution time, notifications to Distribution lists (emails), and more. You can also enable and use multiple plugins at the same time.
- Syntax:
[defaults]
Callback_whitelist = slack, mailProfile_tasks:
This shows the duration of time took to execute each task.

Mail:
It can be configured to monitor the job in case of success / failure. Below is the example.
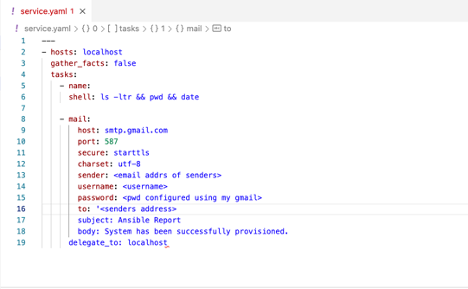
We will receive alerts in email once this playbook gets executed.
Some of the other_plugins are listed below
| Name | Description | Libraries required using pip |
| Foreman | Notifies to Foreman | |
| Hipchat | Notifies to HipChat | Prettytable |
| Jabber | Notifies to Jabber | git+https://github.com/ArchipelProject/xmpppy |
| Junit | Write JUnit-formatted to XML file | Junit_xml |
| Log_plays | Log results per hosts | |
| Logentries | Notifies to Logentries | Certifi flatdict |
| Logstash | Send results to Logstash | Python-logstash |
| Notifies through email when tasks fail | ||
| Osx_say | Speak notifications on macOS | |
| Profile_tasks | execution time for each task | |
| Slack | Notifies to Slack | Prettytable |
| timer | Report total execution time of playbook |
Ref: https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/plugins/callback.htm
About the Author
[table id =5 /]
[post_title] => Ansible Callback Plugins [post_excerpt] => [post_status] => publish [comment_status] => closed [ping_status] => closed [post_password] => [post_name] => ansible-callback-plugins [to_ping] => [pinged] => [post_modified] => 2022-09-23 14:04:43 [post_modified_gmt] => 2022-09-23 14:04:43 [post_content_filtered] => [post_parent] => 0 [guid] => https://keyvatech.com/?p=3379 [menu_order] => 0 [post_type] => post [post_mime_type] => [comment_count] => 0 [filter] => raw ) [1] => WP_Post Object ( [ID] => 3371 [post_author] => 13 [post_date] => 2022-09-15 15:45:00 [post_date_gmt] => 2022-09-15 15:45:00 [post_content] =>Jaime Gmach has been named the recipient of a 2022 Lifetime Achievement Award by Vistage, the world’s largest CEO coaching and peer advisory organization for small and midsize businesses. The Lifetime Achievement Award honors long-standing members who see no finish line in their pursuit of world class. With a track record of bold decisions benefiting company, community and beyond, these members are a beacon to Vistage peers even as they achieve personal greatness.
Jaime Gmach is the founder and Chief Executive Officer of Evolving Solutions, a leading technology solution provider focused on helping enterprise clients modernize and automate their mission-critical infrastructure to support digital transformation. He also serves as CEO of Keyva, which he founded in 2018. Keyva is a services organization focused on cloud automation, orchestration, and DevOps, and was launched to help clients take advantage of innovation and disruptions driven by cloud technologies.
Both organizations thrive due to the commitment to their core values of Do the Right Thing, Be a Team Player, and Be Humbly Confident, highlighted by being named a Top Workplace in Minnesota in 2022. One of Jaime’s true passions in life is giving back to the communities of Minneapolis and St. Paul. He has led multiple Evolving Solutions and Keyva philanthropic initiatives that provide technology, financial, and labor support to charitable organizations throughout the region.
“I am honored and humbled to receive this prestigious award because of the transformational effect of my involvement with Vistage, said Gmach. “It supported me in building strong companies with a foundation of strong values, employee-first cultures and the focus of delivering the best outcomes to our clients.”
“Jaime was selected from over 300 local Vistage members as one who embodies our Vistage values of Growth, Challenge, and Commitment,” said Brian Davis, Vistage Master Chair. “Not only has he built two highly successful and thriving businesses, but he has also had a huge impact on his community and his fellow Vistage group members. In the last 10 years I have seen tremendous growth in him professionally, personally, and spiritually, and he serves as a model of what effective leadership looks like for all of us. I feel blessed to have him in our group!”
About Vistage Worldwide, Inc.
Vistage is the world’s largest CEO coaching and peer advisory organization for small and midsize businesses. For more than 60 years, we’ve been helping CEOs, business owners and key executives solve their greatest challenges through confidential peer groups and one-to-one executive coaching sessions. Today, more than 25,000 members in 25 countries rely on Vistage to help make better decisions for their companies, families, and communities. The results prove it: Vistage CEO members grew their annual revenue on average by 4.6% in 2020, while nonmembers with comparable small and midsize businesses saw revenue decrease by 4.7%, according to a study of Dun & Bradstreet data. Learn more at vistage.com.
About Evolving Solutions
Evolving Solutions helps clients modernize and automate their mission-critical applications and infrastructure to support business transformation. Our business is client-centric consulting and delivery of technical solutions to enable modern operations in a hybrid cloud world. Learn more at www.evolvingsol.com.
About Keyva
At Keyva, we exist today so our clients can thrive tomorrow. This means we do everything we can to provide services and expertise that go beyond IT. We work hard to simplify our clients’ technologies, to free up time so they can focus on their core business. Learn more at www.keyvatech.com.
By: Delroy Hall – Devops Engineer
In this blog we will cover how to install Portworx to be used as a highly available storage solution on Amazon EKS.
What is Portworx:
Portworx is a software defined storage solution designed for container environments. Portworx provides a wide range use case with various application with data protection, data security, data migration and more in mind.
Pre-requisites:
- AWS EKS cluster v1.21+ (To quickly spin up an EKS cluster feel free to follow this guide)
Installing Portworx via Operator:
1. Create an IAM policy using the following permissions and add the policy to your EKS nodegroup(s) role. These are the permissions needed for storage operations.
1. {
2. "Version": "2012-10-17",
3. "Statement": [
4. {
5. "Sid": "",
6. "Effect": "Allow",
7. "Action": [
8. "ec2:AttachVolume",
9. "ec2:ModifyVolume",
10. "ec2:DetachVolume",
11. "ec2:CreateTags",
12. "ec2:CreateVolume",
13. "ec2:DeleteTags",
14. "ec2:DeleteVolume",
15. "ec2:DescribeTags",
16. "ec2:DescribeVolumeAttribute",
17. "ec2:DescribeVolumesModifications",
18. "ec2:DescribeVolumeStatus",
19. "ec2:DescribeVolumes",
20. "ec2:DescribeInstances",
21. "autoscaling:DescribeAutoScalingGroups"
22. ],
23. "Resource": [
24. "*"
25. ]
26. }
27. ]
28. }
29.
2. To install Portworx on a Kubernetes cluster, you will need to generate a Kubernetes manifest file. Navigate to https://central.portworx.com
- You must log in or create a free account for access
3. To generate the manifest file, select Portworx Enterprise from product catalog
4. Under Product Line, select the option depending on your license/use case. For this guide select Portworx Enterprise, then click Continue.
- Portworx Enterprise comes with a 30-day trial
5. Check the box Use the Portworx Operator, select the latest version of Portworx available, and select the Built-in option for ETCD, the click Next.
- When using the Built-in option Portworx will create and manage an internal key-value store cluster.
6. For your environment select Cloud, and AWS Cloud Platform
7. For Configuring storage devices select Create Using a Spec and the following for storage
- EBS Volume Type: GP2
- Size: 150GB (Minimum required)
- Set Max storage nodes per availability zone: 1, then click Next.
8. Under Network keep the default options, then select Next.
9. Under Customize select Amazon Elastic Container Service for Kubernetes (EKS) and click Finish
- You can set your Cluster Name Prefix under Advanced Settings
10. After generating the spec file Portworx will provide you with the following commands to run against your AWS EKS cluster:
- Deploying the Operator
kubectl apply -f 'https://install.portworx.com/2.11?comp=pxoperator’- Deploying Portworx
kubectl apply -f 'https://install.portworx.com/2.11?operator=true&mc=false&b=true&kd=type%3Dgp2%2Csize%3D150&mz=1&s=%22type%3Dgp2%2Csize%3D150%22&c=px-cluster&stork=true&csi=true&mon=true&tel=false&st=k8s&promop=true'The cluster will provision EBS volumes based on our settings and attach them to the nodes.
To verify your install, you can run the following to get Portworx Cluster status:
PX_POD=$(kubectl get pods -l name=portworx -n kube-system -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')
kubectl exec $PX_POD -n kube-system -- /opt/pwx/bin/pxctl status
About the Author
[table id =6 /]
[post_title] => Deploying Portworx on Amazon EKS [post_excerpt] => [post_status] => publish [comment_status] => closed [ping_status] => closed [post_password] => [post_name] => deploying-portworx-on-amazon-eks [to_ping] => [pinged] => [post_modified] => 2024-05-28 18:25:51 [post_modified_gmt] => 2024-05-28 18:25:51 [post_content_filtered] => [post_parent] => 0 [guid] => https://keyvatech.com/?p=3357 [menu_order] => 0 [post_type] => post [post_mime_type] => [comment_count] => 0 [filter] => raw ) [4] => WP_Post Object ( [ID] => 3335 [post_author] => 7 [post_date] => 2022-08-23 18:54:15 [post_date_gmt] => 2022-08-23 18:54:15 [post_content] =>By: Saikrishna Madupu – Sr Devops Engineer
In this blog, we will cover what is Goss, and how to leverage it for automated server validation testing.
What is Goss:
Goss is a YAML based serverspec alternative tool for validating a server’s configuration. It eases the process of writing tests by allowing the user to generate tests from the current system state. Once the test suite is written they can be executed, waited-on, or served as a health endpoint. You can do server validation quickly and easily with Goss and integrate with pipelines to monitor the status of any services.
I’ll be using airflow for a target test case. First, we will install airflow locally and validate the status of airflow service status using Goss.
https://github.com/aelsabbahy/goss
Goss Installation:
- OPTION 1:
curl -L https://github.com/aelsabbahy/goss/releases/download/v0.3.7/goss-linux-amd64 -o /usr/local/bin/goss
curl -L https://raw.githubusercontent.com/aelsabbahy/goss/master/extras/dgoss/dgoss -o /usr/local/bin/dgoss
chmod +rx /usr/local/bin/dgoss- OPTION 2:
https://ports.macports.org/port/goss/
Install Macports and run
sudo port install goss
## Add the following line to your ~/.profile or .zshrc
export GOSS_PATH=/usr/local/bin/goss
Use Case:
We will deploy Apache Airflow locally and validate the status of webserver using Goss. Airflow is an open-source project used to programmatically author, schedule, and monitor workflows. You can find more about airflow here - https://airflow.apache.org/
export AIRFLOW_HOME=~/airflow
pip3 install apache-airflow
pip3 install typing_extensions
# initialize the database
airflow initdb
# start the web server, default port is 8080
airflow webserver -p 8080
# start the scheduler. I recommend opening up a separate terminal \
# window for this step
airflow scheduler
# open localhost:8080 in the browser and enable the example dag via the home page
Validation:
Goss.yaml file validates HTTP response status code and content
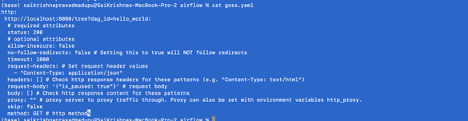
export GOSS_USE_ALPHA=1
goss validate goss.yaml

- As the webserver is not up and running we see the error above
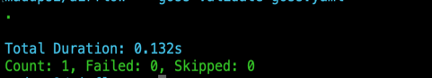
After starting the airflow webserver and making sure the application is up and running by validating it (via opening the page in a browser)
- goss validate goss.yaml would return the status report as shown below.
- Goss also supports several other test cases. Some of those are listed below:
- Addr
- Command
- Dns
- Ount
- Package
- Service
Ref: https://github.com/aelsabbahy/goss/blob/master/docs/manual.md#goss-test-creation
About the Author
[table id =5 /]
[post_title] => GOSS Server Validation [post_excerpt] => [post_status] => publish [comment_status] => closed [ping_status] => closed [post_password] => [post_name] => goss-server-validation [to_ping] => [pinged] => [post_modified] => 2022-08-23 22:00:44 [post_modified_gmt] => 2022-08-23 22:00:44 [post_content_filtered] => [post_parent] => 0 [guid] => https://keyvatech.com/?p=3335 [menu_order] => 0 [post_type] => post [post_mime_type] => [comment_count] => 0 [filter] => raw ) [5] => WP_Post Object ( [ID] => 3302 [post_author] => 7 [post_date] => 2022-08-05 16:35:20 [post_date_gmt] => 2022-08-05 16:35:20 [post_content] =>Keyva is pleased to announce the certification of our ServiceNow App for Red Hat Ansible against the latest ServiceNow San Diego release. This release is the newest updated software version since the company's inception.
Customers can now seamlessly upgrade their ServiceNow App from previous ServiceNow releases (Quebec, Rome) to the San Diego release.
Learn more about the Keyva ServiceNow App for Ansible and view all the ServiceNow releases for which it has been certified at the ServiceNow store, visit https://bit.ly/ansible_servicenow.
[post_title] => ServiceNow App for Red Hat Ansible - Certified for San Diego Release [post_excerpt] => [post_status] => publish [comment_status] => closed [ping_status] => closed [post_password] => [post_name] => servicenow-app-for-red-hat-ansible-certified-for-san-diego-release-2 [to_ping] => [pinged] => [post_modified] => 2024-05-28 18:29:55 [post_modified_gmt] => 2024-05-28 18:29:55 [post_content_filtered] => [post_parent] => 0 [guid] => https://keyvatech.com/?p=3302 [menu_order] => 0 [post_type] => post [post_mime_type] => [comment_count] => 0 [filter] => raw ) [6] => WP_Post Object ( [ID] => 3282 [post_author] => 15 [post_date] => 2022-07-28 17:40:42 [post_date_gmt] => 2022-07-28 17:40:42 [post_content] =>In this blog we will be discuss best practices to handle Kubernetes security by implementing Kyverno policies. We’ll be using a KIND cluster to demonstrate our use cases.
What is Kyverno:
Kyverno is a policy engine (controller) which applies policies to Kubernetes resources. It helps to verify if deployments are adhering to defined standards, and to implement best practices by defining certain conditions (policies). It includes many features, and some of the benefits (not an exhaustive list) are listed below:
- Define policies as Kubernetes resources (no new language to learn!)
- Validate, mutate, or generate any resource
- Verify container images for software supply chain security
- Inspect image metadata
- Match resources using label selectors and wildcards
- Validate and mutate using overlays (like Kustomize!)
- Synchronize configurations across Namespaces
- Block non-conformant resources using admission controls, or report policy violations
- Test policies and validate resources using the Kyverno CLI, in your CI/CD pipeline, before applying to your cluster
- Manage policies as code using familiar tools like git and kustomize
How it Works:
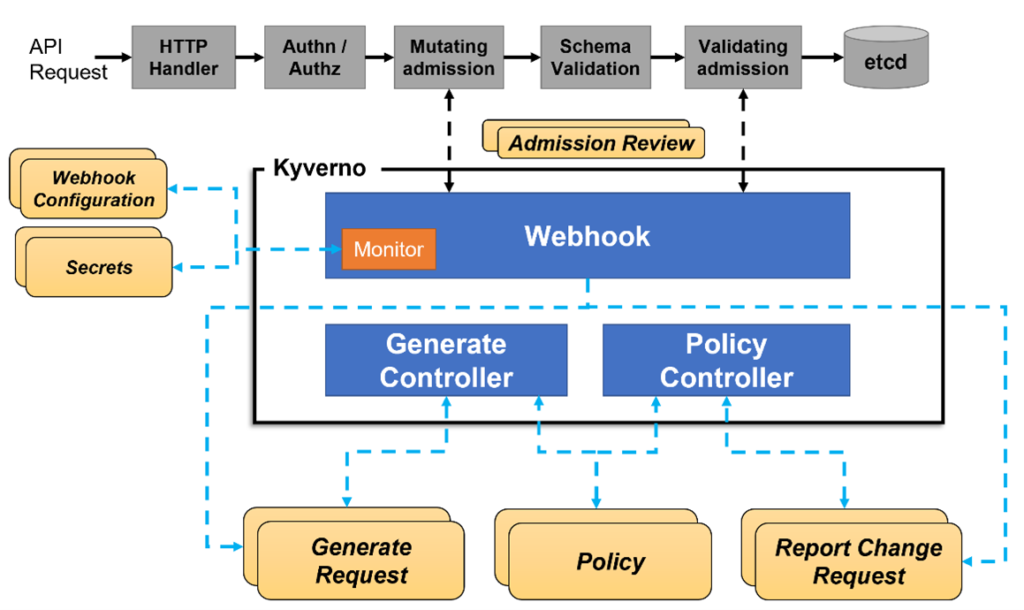
Kyverno runs as an admission controller within the Kubernetes cluster. When Kyverno policies are applied to the cluster and someone tries to deploy any of the resources in that cluster, Kyverno receives the request, validates via mutating admission webhook HTTPS callbacks from the kube-apiserver, and applies matching polices to return results that enforce admission policies or reject requests.
Here is the overall workflow -
Installation: Kyverno can be installed using either helm or yaml file.
Option1:
kubectl create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kyverno/kyverno/main/definitions/release/install.yaml
Option2:
helm repo add kyverno https://kyverno.github.io/kyverno/
helm repo update
helm install kyverno-policies kyverno/kyverno-policies -n kyverno
Use Cases:
We will walkthrough the following examples:
- Disallow the creation of pods in default namespaces
- Restricting the pods if they are not labeled during deployment
- Adding default labels as part of any resource that gets created
- Disallow the creation of pods in default namespaces
We will define restrict-default.yaml as below
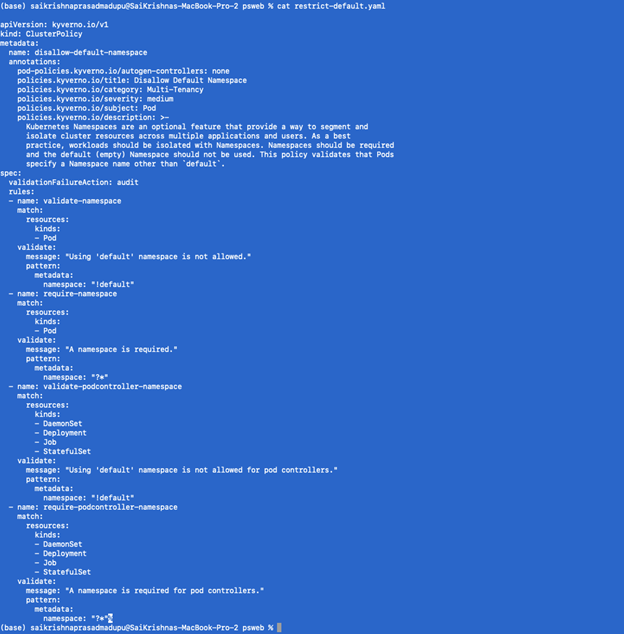
Next, we will apply this policy
Kubectl apply -f restrict-default.yaml
In the below screenshot you can see the steps on how to validate that the appropriate Kyverno policy was applied to the deployment.
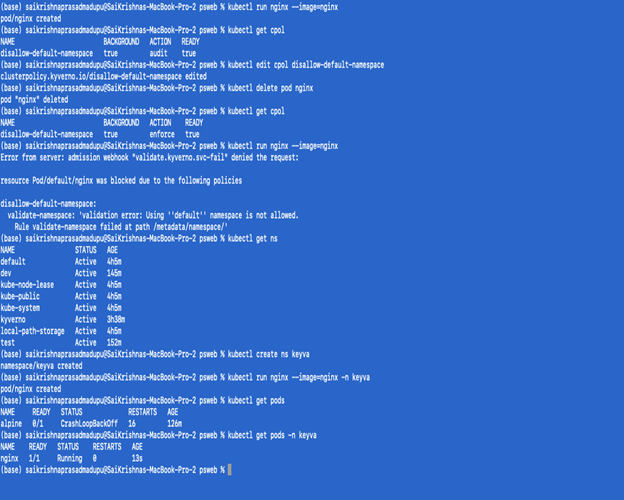
Note:
- If you notice the policy is not in an active state, try again with setting the action state to enforced.
- Deleting the policies:
- Kubectl delete cpol –all
- Ref: https://kyverno.io/docs/introduction/
- Restricting the pods if they are not labeled during deployment:
We will define require-labels.yaml as follows
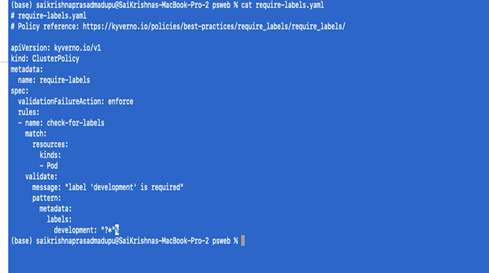
kubectl apply -f require-labels.yaml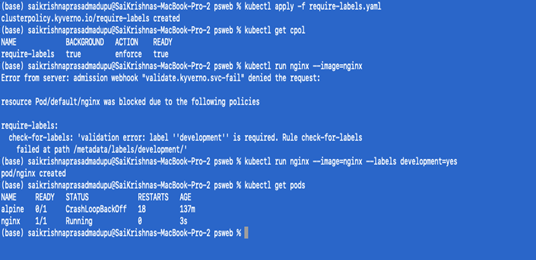
Adding default labels as part of any resource that gets created:
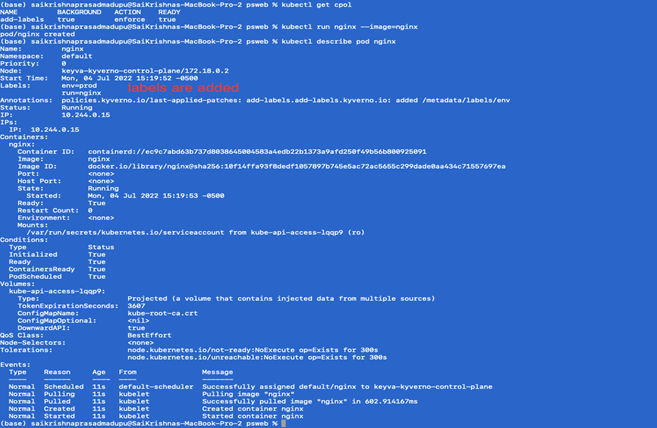
To configure a mutate policy of our KIND Cluster’s ClusterPolicy, and add labels such as env: prod on pods and other resources creation, create default-label.yaml as per below:
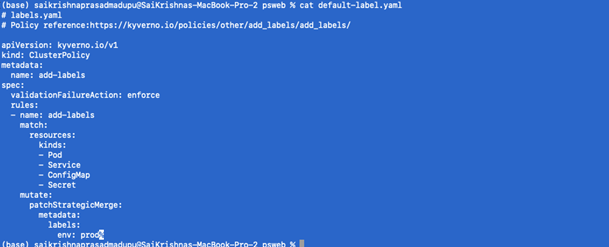
- Apply the policy
Kubectl apply -f default-label.yaml
Keyva is pleased to announce the certification of our ServiceNow App for the Red Hat OpenShift against San Diego release. This release is the newest updated software version since the company's inception.
Customers can now seamlessly upgrade their ServiceNow App for OpenShift from previous ServiceNow releases (Quebec, Rome) to the San Diego release.
Learn more about the Keyva ServiceNow App for Red Hat OpenShift and view all the ServiceNow releases for which it has been certified at the ServiceNow store, visit https://bit.ly/openshift_servicenow.
[post_title] => ServiceNow App for Red Hat OpenShift - Certified for San Diego Release [post_excerpt] => [post_status] => publish [comment_status] => closed [ping_status] => closed [post_password] => [post_name] => servicenow-app-for-red-hat-openshift-certified-for-san-diego-release [to_ping] => [pinged] => [post_modified] => 2024-05-28 18:21:35 [post_modified_gmt] => 2024-05-28 18:21:35 [post_content_filtered] => [post_parent] => 0 [guid] => https://keyvatech.com/?p=3273 [menu_order] => 0 [post_type] => post [post_mime_type] => [comment_count] => 0 [filter] => raw ) ) [post_count] => 8 [current_post] => -1 [before_loop] => 1 [in_the_loop] => [post] => WP_Post Object ( [ID] => 3379 [post_author] => 7 [post_date] => 2022-09-22 20:34:51 [post_date_gmt] => 2022-09-22 20:34:51 [post_content] =>By: Saikrishna Madupu – Sr Devops Engineer
Ansible by Red Hat is the de-facto tool used by organizations for automated configuration management. It is commonly used for use cases around infrastructure deployment and post deployment actions, application deployments, and for infrastructure operations and lifecycle tasks.
In the following blog, we will cover some examples ansible callback plugins, which help us track events around playbook executions. You can use these plugins for notification of task failures, job statuses, etc.
Features:
- Stdout plugins
- Other Plugins (also includes notification plugins & aggregate plugins in general)
A complete list of available plugins can be viewed from terminal:
ansible-doc -t callback -l
Stdout_plugins:
- This can be configured by adding stdout_callback plugin as a parameter in your ansible.cfg under defaults section. These plugins are limited to use one at a time.
- Syntax:
[defaults]
stdout_callback = actionable- Some stdout_plugins are listed below:
| Name | Description |
| Actionable | Changed/failed status |
| Default | Default o/p |
| debug | Readable stderr & stdout |
| Dense | Overwrite o/p rather than scrolling |
| Json | Json o/p |
| Minimal | Task details with proper format |
| Selective | o/p for tagged task |
| Skippy | Doesn’t show o/p for skipped hosts |
| Oneline | Similar to Minimal but in one line |
Examples of usage:
Actionable:
This plugin is deprecated.
Op:
- community.general.actionable has been removed. Use the 'default' callback plugin with 'display_skipped_hosts = no' and 'display_ok_hosts = no' options. This feature was removed from community.general in version 2.0.0. Please update your playbooks.
Debug:
By enabling debug plugin we don’t need to register output and use again debug module in our playbooks.

Default:
Displays standard error in human readable format

Dense:
It overwrites o/p and only shows two lines as shown below.

JSON:
Prints o/p in json format and we see the entire o/p.

Minimal:
It is quite similar to default,

Selective:
Selective plugin shows o/p for tasks that got executed successfully that are tagged with print_action

Skippy:
It doesn’t show o/p for the tasks that got skipped, when a task is not executed for any sort of host it will not be displayed as skipped likewise default do in cases.

Oneline:
It shows o/p of command in one format as shown below.

Other plugins:
- There are several other plugins which can send alerts in case of job failures to slack channels, records job execution time, notifications to Distribution lists (emails), and more. You can also enable and use multiple plugins at the same time.
- Syntax:
[defaults]
Callback_whitelist = slack, mailProfile_tasks:
This shows the duration of time took to execute each task.

Mail:
It can be configured to monitor the job in case of success / failure. Below is the example.

We will receive alerts in email once this playbook gets executed.
Some of the other_plugins are listed below
| Name | Description | Libraries required using pip |
| Foreman | Notifies to Foreman | |
| Hipchat | Notifies to HipChat | Prettytable |
| Jabber | Notifies to Jabber | git+https://github.com/ArchipelProject/xmpppy |
| Junit | Write JUnit-formatted to XML file | Junit_xml |
| Log_plays | Log results per hosts | |
| Logentries | Notifies to Logentries | Certifi flatdict |
| Logstash | Send results to Logstash | Python-logstash |
| Notifies through email when tasks fail | ||
| Osx_say | Speak notifications on macOS | |
| Profile_tasks | execution time for each task | |
| Slack | Notifies to Slack | Prettytable |
| timer | Report total execution time of playbook |
Ref: https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/plugins/callback.htm
About the Author
[table id =5 /]
[post_title] => Ansible Callback Plugins [post_excerpt] => [post_status] => publish [comment_status] => closed [ping_status] => closed [post_password] => [post_name] => ansible-callback-plugins [to_ping] => [pinged] => [post_modified] => 2022-09-23 14:04:43 [post_modified_gmt] => 2022-09-23 14:04:43 [post_content_filtered] => [post_parent] => 0 [guid] => https://keyvatech.com/?p=3379 [menu_order] => 0 [post_type] => post [post_mime_type] => [comment_count] => 0 [filter] => raw ) [comment_count] => 0 [current_comment] => -1 [found_posts] => 134 [max_num_pages] => 17 [max_num_comment_pages] => 0 [is_single] => [is_preview] => [is_page] => [is_archive] => [is_date] => [is_year] => [is_month] => [is_day] => [is_time] => [is_author] => [is_category] => [is_tag] => [is_tax] => [is_search] => [is_feed] => [is_comment_feed] => [is_trackback] => [is_home] => 1 [is_privacy_policy] => [is_404] => [is_embed] => [is_paged] => 1 [is_admin] => [is_attachment] => [is_singular] => [is_robots] => [is_favicon] => [is_posts_page] => [is_post_type_archive] => [query_vars_hash:WP_Query:private] => 4b6a14939efc61b5c6c83cb73e278a35 [query_vars_changed:WP_Query:private] => [thumbnails_cached] => [allow_query_attachment_by_filename:protected] => [stopwords:WP_Query:private] => [compat_fields:WP_Query:private] => Array ( [0] => query_vars_hash [1] => query_vars_changed ) [compat_methods:WP_Query:private] => Array ( [0] => init_query_flags [1] => parse_tax_query ) [query_cache_key:WP_Query:private] => wp_query:5e1e8ce45a8275c4f91f8fe4a8e5b39e:0.69800800 1751001635 [tribe_is_event] => [tribe_is_multi_posttype] => [tribe_is_event_category] => [tribe_is_event_venue] => [tribe_is_event_organizer] => [tribe_is_event_query] => [tribe_is_past] => )






